When we talk about space, it often sounds like fiction at first. However, we are not as far away as we may think. A new security testing trend that is flourishing nowadays is the well known Pentest against satellites. Today, a single person can design, build and launch a satellite while respecting very few safety standards and protocols.
As we already know, human error is quite well known in our field, which together with the democratization of space that has opened a new frontier to companies and enthusiasts to exploration and innovation in the space field, produces the birth of a new set of specific vulnerabilities, which require qualified and specialized professionals to identify them.
What is Satellite Pentesting?
In short, it is what many of us already know as “pentesting” but extrapolated to satellites. Therefore, it is a process of testing the security of satellite communication systems, where we simulate attacks against them, identifying potential vulnerabilities and deficiencies that can be exploited and then report them to the client with their respective corrective measures, allowing them to mitigate the risks identified.
Type of satellite vulnerabilities
Satellites present several vulnerabilities. First, they are controlled from the ground by people, and their information is transmitted to and from the ground. Therefore, accessing their networks is usually “easier” than if there were a single point of entry.
From this we understand that there are three key points where possible cyber-attacks can occur:
- Terrestrial Infrastructure: the location where space assets (ground stations, terminals, users) are located.
- The satellites themselves.
- The supply chain, understood as everything related to satisfy the correct satellite communication.
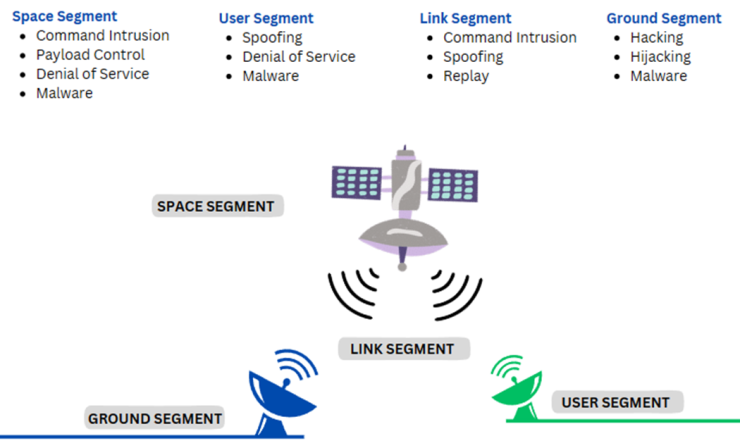
Related to this last point, satellites involve multiple manufacturers and system integrators so that all components function properly as one. Such a multiplicity of vendors provides the opportunity for an attacker to gain access to the system through several potential routes.
To this end, there is a matrix called Space Attack Research and Tactic Analysis (SPARTA), which compiles all Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTP) in terms of cyberspace attacks. In this, a knowledge base of adversary behaviors and the actions they would take throughout the life cycle of such an attack can be found.

Based on the matrix provided by SPARTA, we identify the most common attacks that are usually performed and the security tests that are usually performed in this context.
Common types of attacks
- Jamming Attacks
- Replay Attacks
- Man-in-The-Middle (MiTM) attacks
- Attacks against Authentication
- Physical attacks
Types of tests typically performed
- Satellite signal interception and analysis.
- Ground Station security evaluation.
- Protocol analysis and vulnerability assessment.
- Jamming and Spoofing resistance tests.
- Physical security evaluations.
- Red Team exercises.
- Social Engineering evaluations.
- Regulatory compliance audits in satellite standards.
Case Studies
- ROSAT (1998). They take control of NASA’s ROSAT X-ray scientific satellite, causing it to turn towards the sun and disabling the satellite’s batteries and optics (Ground Segment Attack).
- LANDSAT 7 (2007, 2008). Attempted Chinese takeover of the LANDSAT 7 satellite (Link Segment Attack).
- TERRA EOS AM-1 (2008). Chinese takeover of the Terra EOS AM-1 satellite (Link Segment Attack).
Basic Satellite Pentest
The first thing to keep in mind when dealing with tests of this style is to have the right tools. Although the set of tools may vary from case to case, in general we can start from the set of tools below:

The methodology to be applied in this type of tests can be something like:
- Identify the “satellite communication” of the system to be audited.
- Prepare the test base, i.e. the type of attack to be performed (Jamming, Spoofing, MiTM, DoS, Unauthorized Access).
- Configure the Toolset to suit the needs of the audit. Install the SDR receiver, satellite dish, GPS receiver, etc.
- Use the Toolset you have configured to locate the satellite and intercept the signals it transmits.
- Analyze the intercepted signals.
- Identify potential vulnerabilities and deficiencies in the satellite communication.
- Prepare a report with the identified deficiencies and their respective corrective measures to mitigate such risks.
This methodology is not intended to be unique and should be adjusted to the scenario as an auditor.
Conclusion
As cybersecurity analysts, we often face new challenges on a daily basis. This new aspect (Satellite Pentesting) opens a new complex and challenging challenge, which requires special knowledge of satellite communications, specialized hardware and software, as well as some expertise in the subject.
Nowadays, satellite communications play a fundamental role in everyday life and their importance will continue to grow in the future. It is therefore of vital importance to ensure the security of these communication systems against potential cyber-attacks.
It is not very difficult for a “hacker” to move from cyberspace to space. In this article we have not wanted to go into more complex contexts, such as satellite communication, the development of a satellite C2, etc. The purpose has been to inform about this topic and to sow the seed of curiosity about it. Dear reader, I encourage you to investigate and enter into this new world, which is becoming more and more extensive every day.
